
안드로이드에서 뷰는 위젯의 가장 기본이며 여러 UI 컴포넌트(Button, TextView, EditText, ...)와 상호작용하는데 사용된다. 안드로이드 위젯은 대부분 앱을 만들기에 충분히 많은 것들을 제공하고 있지만, 부족한 경우 커스텀 위젯을 스스로 만들어 사용 할 수도 있다.
대부분의 안드로이드 프레임워크 뷰 클래스는 'View'를 상속하고 있다. 마찬가지로 커스텀 뷰도 'View'를 상속하거나 View의 서브클래스중 하나(Button, TextView, ...)를 상속하여 시간을 절약 할 수도 있다.
따라서 커스텀 뷰를 만들기 전에 'View'가 뭔지 우선 이해하고 시작해야 한다.
그래서 View가 뭘까?
앞서 말했듯이, View는 위젯의 가장 기본이며 여러 UI 컴포넌트(Button, TextView, EditText, ...)와 상호작용하는데 사용된다. 이때 layout도 view의 subclass로, 다른 뷰를 포함할 수 있고 레이아웃 속성을 정의하지만 보이지 않는 컨테이너이다.
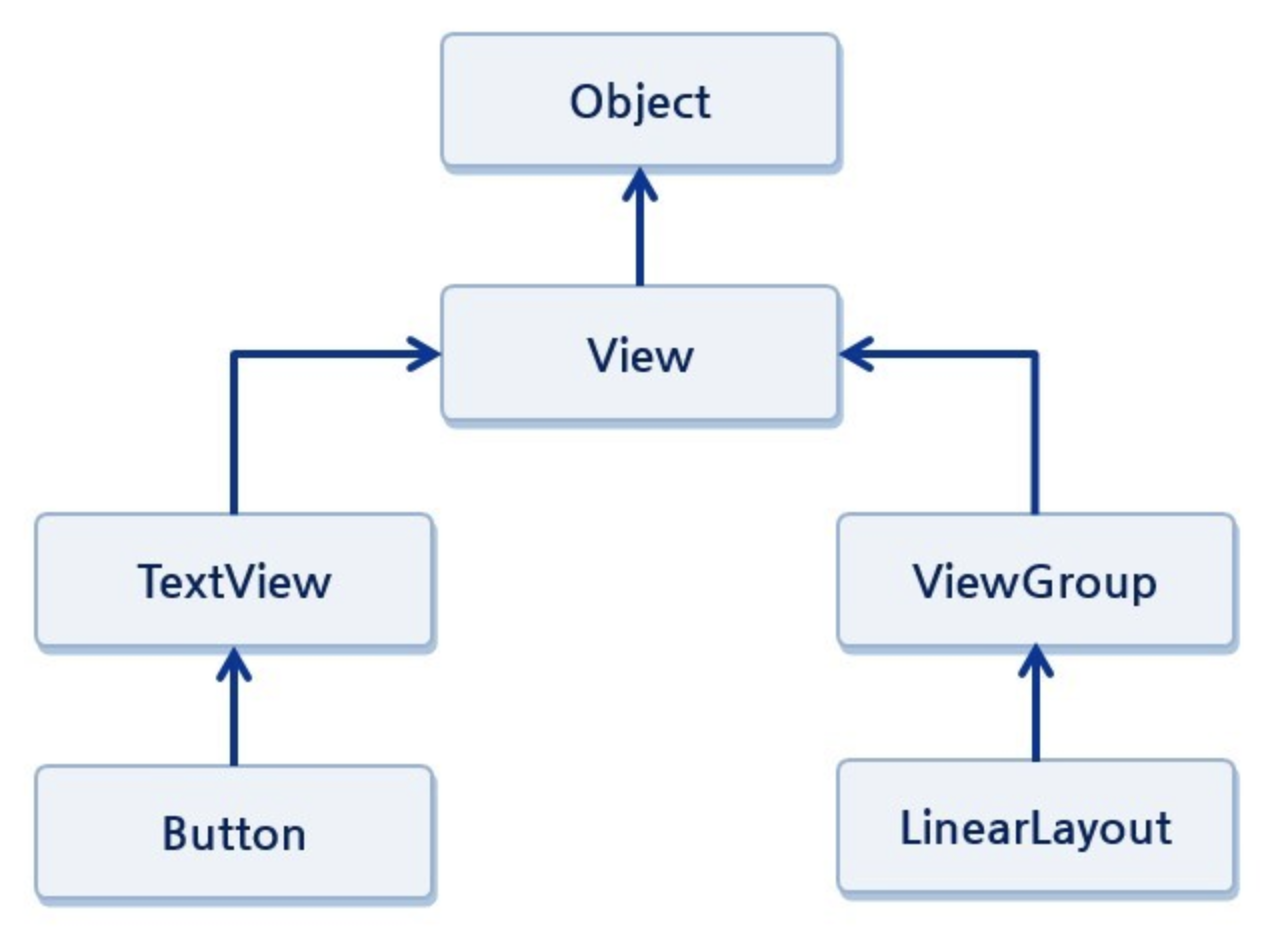
뷰는 안드로이드 기본 화면을 구성하는 모든 기본 화면 구성요소를 말한다.
눈에 보이지 않는 것도 있긴 하지만 눈에 보이는 각각의 것들을 뷰라고 이해할 수 있다.
뷰 중에 눈에 보이지 않는 것들이 있다 보니 눈에 보이는 것들은 위젯, 눈에 보이지 않는 것들은 레이아웃이라고 구분한다.
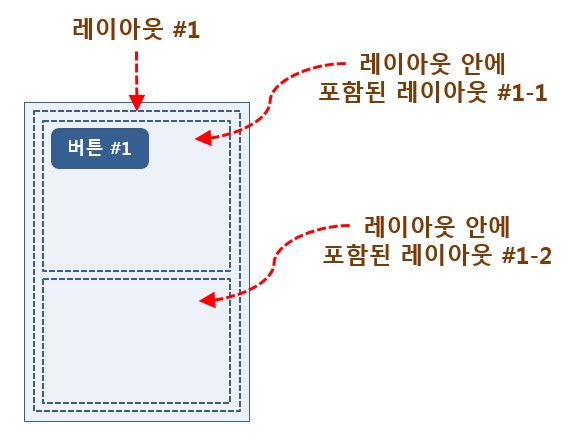
레이아웃은 그 안에 다른 뷰들을 담아둘 수 있는데 레이아웃도 뷰를 상속하여 정의되었기 때문에 레이아웃 안에 레이아웃도 담을 수 있다.
즉, 레이아웃 안에 레이아웃, 다시 그 레이아웃 안에 레이아웃을 넣는 방식을 사용하는 것이 뷰 속에 뷰를 계속 담아가는 것이다.
View Lifecycle
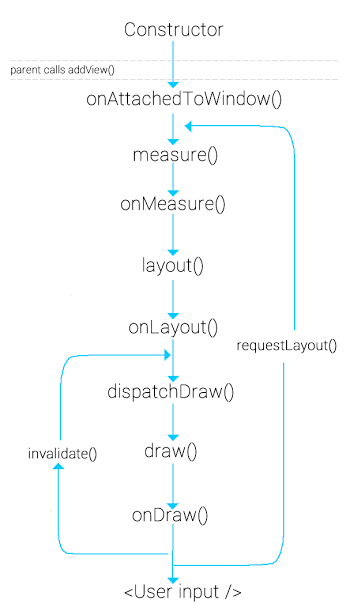
커스텀 뷰를 구현하려면 꼭 'View' 클래스를 상속해야 한다.
이렇게 상속을 하고나면 custom view는 다양한 Overrides를 제공해주는데 아래 테이블로 표시해 두고자 한다.
|
CATEGORY |
METHODS |
DESCRIPTION |
|
Creation |
Constructors |
There is a form of the constructor that are called when the view is created from code and a form that is called when the view is inflated from a layout file. The second form should parse and apply any attributes defined in the layout file. |
|
`onFinishInflate()` |
Called after a view and all of its children has been inflated from XML. |
|
|
Layout |
`onMeasure(int, int)` |
Called to determine the size requirements for this view and all of its children. |
|
`onLayout(boolean, int, int, int, int)` |
Called when this view should assign a size and position to all of its children. |
|
|
`onSizeChanged(int, int, int, int)` |
Called when the size of this view has changed. |
|
|
Drawing |
`onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)` |
Called when the view should render its content. |
|
Event processing |
`onKeyDown(int, KeyEvent)` |
Called when a new hardware key event occurs. |
|
`onKeyUp(int, KeyEvent)` |
Called when a hardware key up event occurs. |
|
|
`onTrackballEvent(MotionEvent)` |
Called when a trackball motion event occurs. |
|
|
`onTouchEvent(MotionEvent)` |
Called when a touch screen motion event occurs. |
|
|
Focus |
`onFocusChanged(boolean, int, android.graphics.Rect)` |
Called when the view gains or loses focus. |
|
`onWindowFocusChanged(boolean)` |
Called when the window containing the view gains or loses focus. |
|
|
Attaching |
`onAttachedToWindow()` |
Called when the view is attached to a window. |
|
`onDetachedFromWindow()` |
Called when the view is detached from its window. |
|
|
`onWindowVisibilityChanged(int)` |
Called when the visibility of the window containing the view has changed. |
https://codentrick.com/android-view-lifecycle/
Android View Lifecycle
[/content/images/2015/07/android_view_hierarchy.png] In Android, View class is the base for widgets, which are used to create interactive UI components(Button, TextView, EditText,…). Android’s widgets are sufficient for the needs of most apps. However, the
codentrick.com
https://www.edwith.org/boostcourse-android/lecture/17039
'Basic > Android' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Matrix를 이용한 resize bitmap in layout (0) | 2019.11.05 |
|---|---|
| Android bitmap recycle 개념 및 방법 (0) | 2019.11.03 |
| Android matrix를 이용한 간단한 연습 (0) | 2019.11.02 |
| 안드로이드 Log 사용 방법 (0) | 2019.10.31 |
| MainHandler와 ThreadHandler를 통한 통신 예제 (0) | 2019.10.26 |